Osteochondrosis is a medical term that describes a violation of the integrity of the cartilaginous surfaces of the bones. The disease is most often associated with damage to the intervertebral discs.
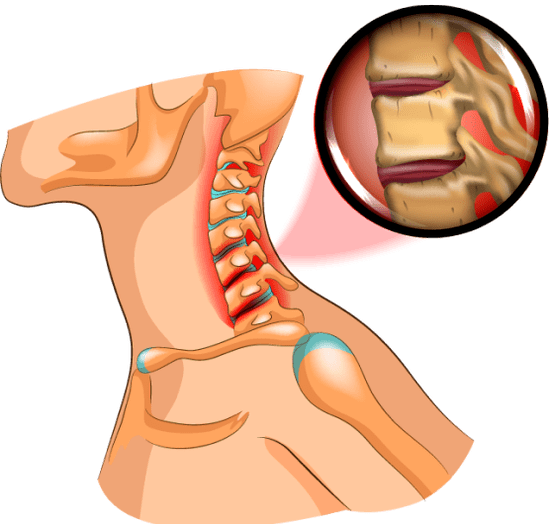
Intervertebral discs are a kind of shock absorbers that soften the pressure on the spine under load. Osteochondrosis worsens the quality of life, causing pain in the back, neck, head, and tinnitus.
There are two points of view regarding the diagnosis. Experts abroad attribute this disorder to childhood and adolescent diseases. It is believed to be more common in children because their bones are in a developmental stage. Russian doctors diagnose osteochondrosis mainly in patients aged 25 to 55 years. The signs, causes and types of the disease in the two cases are the same.
How to define osteochondrosis?
- Are there persistent or recurrent back pain or muscle tension?
- Do you have chills in your lower back or neck?
- Do you feel a "shot" in your back?
- Do you feel pain when you raise your arms or shake your head to the side?
- Do you have occasional dizziness?
- Do you experience bouts of noise, nausea?
If at least one answer is yes, it is worth contacting an expert to conduct the study. If the diagnosis reveals a violation, the doctor will prescribe treatment and protect yourself from more serious and painful symptoms.
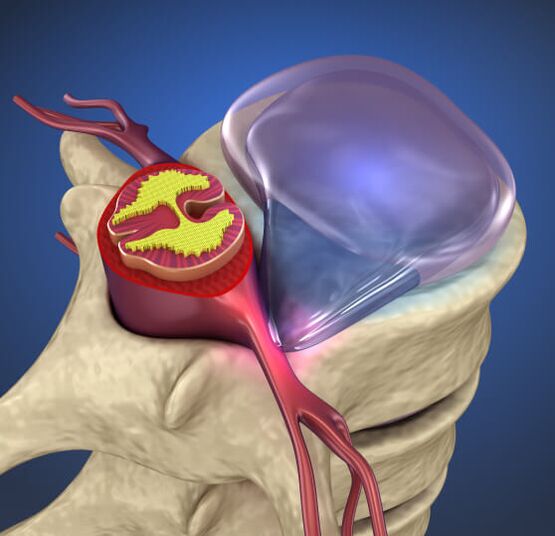
What causes osteochondrosis
The huge incidence of osteochondrosis is related to the fact that people are in an upright position most of the time. In this case, the spine and discs are under increased stress. If they sit, lie down and stand incorrectly, the discs lose the ability of the pillow.
Over time, the disc lining ruptures and hernial protrusions appear. They begin to squeeze out blood vessels, spinal cord roots, or the brain itself. As a result, there is pain, reflex tension in the muscles.
The risk group includes middle-aged and elderly people. Office workers, professional drivers, tall people are most often faced with this disease. Risk factors for the onset of severe symptoms of the disorder may be:
- flat feet;
- heredity;
- overweight;
- hypodynamics.
Reasons for the appearance of disorders in the articular cartilage:
Heavy load handling.
Improper posture while sitting, standing or lying down.
Injuries, excessive strain.
Excessive stress when playing sports.
High humidity and low temperature.
Activities associated with frequent changes in body position.
Types of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis can develop in any part of the spine. By localization, the disease is divided into: cervical, thoracic and lumbar. The latter type occurs in 50% of cases.
Lumbar osteochondrosis

A similar diagnosis is made for both men and women. The reason for this is the increased load that occurs during long walks, running, exercising and sitting. The lumbar spine consists of 5 vertebrae, between which there are discs that give elasticity. If the metabolic process does not occur, the intervertebral discs lose their properties and pain occurs.
Symptoms:
- Dull or sharp back pain that worsens with movement.
- Pain in the legs, pelvic organs, sacral region.
- Impaired mobility or sensitivity.
- Leg muscle atrophy in the acute course of the disease.
Lumbar osteochondrosis must be treated. In the absence of therapy, dangerous complications can occur: sciatica, hernia, bulge. As a result, the natural supply to the spinal cord is disrupted, leading to paralysis of the lower limbs.
Cervical osteochondrosis
"Be sure to turn your head" - doctors call. This way you can avoid the dangerous diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The neck is the most mobile part of the spine. The department consists of 7 vertebrae. The disease occurs as a result of metabolic disorders in the body, in the presence of salt in the neck or due to frequent uncomfortable head position.
Symptoms:
- Headache;
- Pain in the heart area;
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes;
- Hearing damage;
- Crunching of the cervical spine;
- Pain in the wrist or shoulder;
- Numbness of the limbs.
Experts note that this type of disease is one of the most dangerous, because it can cause poor circulation in the brain, migraine, dystonia and more serious diseases.
Osteochondrosis of the chest
Disorders in the thoracic spine occur less frequently because the vertebrae are inactive. The pain that occurs in this part of the body is experienced by many people who engage in heavy physical work or have a sedentary profession. The cause of osteochondrosis can be a disturbed metabolic process, increased load on the intervertebral discs.
Symptoms:
- Chest pain or tightness.
- Pain between the shoulder blades when raising the arms.
- Skin sensitivity disorders.
Two symptoms can occur in an acute disorder: dorsago and dorsalgia. Dorsago is accompanied by acute chest pain, shortness of breath. With dorsalgia, the pain in the vertebral region of the ward is not too severe, but gradually intensifies. The disease is often confused with other pathologies in the chest: heart attack, pneumonia, angina pectoris, etc. The diagnosis is made only by a specialist, based on examinations and research.
Stages of osteochondrosis
- There are no obvious symptoms in the first stage. Periodically, there is discomfort in the spine that is associated with fatigue or excessive physical exertion. The disease can be detected during a routine examination, X-ray or CT examination.
- The second phase is followed by the pain syndrome, because the process of destroying the cartilage tissue begins and the gap between the discs is reduced. Pain at this stage is relieved by medications prescribed by a doctor.
- In the third phase, spinal deformities begin: the fibrous ring is broken, and an intervertebral hernia appears. With the help of properly prescribed treatment, it is still possible to improve the condition of the spine.
- The fourth phase is irreversible changes in the spine, in which it becomes difficult for a person to move. Bone tissue grows between the vertebrae, connecting the vertebrae. This form of osteochondrosis usually leads to disability.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the extent of the disease, check sensitivity and reflexes, the doctor performs a physical examination. In addition, blood and urine tests are taken, and indicators of calcium metabolism are studied.
Diagnostic methods are used to make an accurate diagnosis:
- Vascular ultrasound. Determining the degree of impaired blood flow in the spinal arteries.
- X-ray of the spine.
- UKT. Construction of a three-dimensional image of the test area to detect small vertebral displacements.
- DIE. Soft tissue condition study to assess the condition of the spinal cord and visualize the internal structure of the discs.
Treatment

Osteochondrosis is treated in a comprehensive way. The main goal of therapy is to suppress painful sensations, remove muscle tension and stiffness of movements that occur due to pain. It is important not to engage in self-medication, but to consult an expert and follow the recommendations.
To treat the spine, the doctor prescribes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to help alleviate inflammation and swelling. Muscle relaxants are responsible for reducing muscle cramps. Ointments are used to relieve pain. Antioxidants and vitamins may be prescribed to protect nerve tissue.
Prophylaxis

Preserve the health of the spine and prevent the appearance of symptoms or complications of osteochondrosis by adhering to the method of prevention:
- drinking enough water, weight control;
- eat foods rich in collagen;
- the choice of an orthopedic mattress that supports the body;
- regular exercise.
Alternative methods can be tried: acupuncture, qigong or massage. Before starting any procedure, you should consult a doctor to guarantee the health of the musculoskeletal system.























